You're diving deep into the world of Ethernet cables! It's true that they might all look the same from the outside, but there are important differences in their capabilities.
Common Types of Cables
Ethernet cables are categorized (Cat) based on their performance, primarily speed and frequency. Here's a table summarizing the main types:
| Category | Max Speed | Max Frequency | Max Distance | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz | 100 meters | Mostly obsolete; replaced by Cat 5e |
| Cat 5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100 meters | Common for home networks and older offices |
| Cat 6 | 1 Gbps | 250 MHz | 100 meters (10 Gbps up to 55 meters) | Faster speeds and better performance than Cat 5e |
| Cat 6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100 meters | High-performance networks; data centers |
| Cat 7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100 meters | Even higher performance; less common |
| Cat 7a | 10 Gbps | 1000 MHz | 100 meters (40 Gbps up to 50 meters, 100 Gbps up to 15 meters) | Top-tier performance, future-proof; expensive |
| Cat 8 | 40 Gbps | 2000 MHz | 30 meters (shorter distances) | Latest standard; very high speeds for data centers |
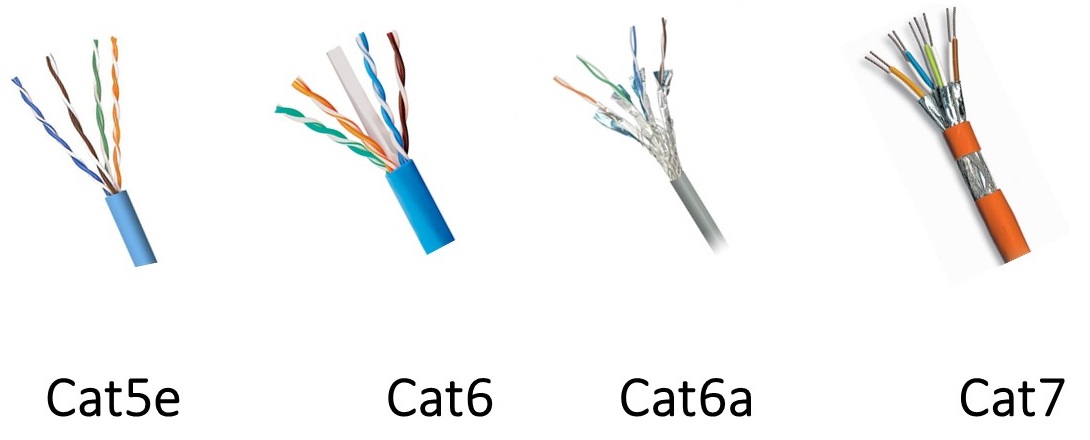
Shielding
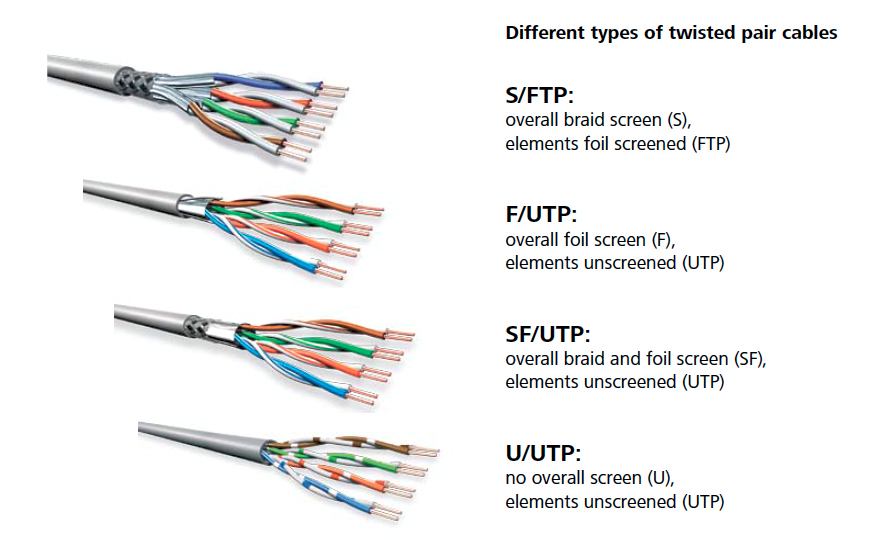
Besides the category, Ethernet cables also differ in their shielding:
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): No shielding. Most common and affordable.
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Each pair has a foil shield to reduce interference. Less common.
- FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair): Overall foil shield for the cable.
- S/FTP (Screened Foiled Twisted Pair): Individual and overall shielding for maximum protection.
Which Cable Do You Need?
This really depends on your needs:
- Home use: Cat 5e or Cat 6 is generally sufficient for most home networks.
- Gaming or high-bandwidth activities: Cat 6 or Cat 6a for faster speeds and lower latency.
- Future-proofing: Cat 6a or Cat 7 for higher bandwidth needs in the future.
- Data centers: Cat 6a, Cat 7a, or Cat 8 for high-performance networks.
Important Notes:
Backward compatibility: Higher category cables generally work with lower category equipment, but you'll
only get the speed of the lower category.
Cable length: Signal quality degrades over distance. Use shorter cables for best performance.
I hope this helps you understand the differences between Ethernet cable types. It's always best to choose
a cable that meets your current needs and provides some room for future upgrades.



